The Broadband Fabric Location Data Suite is a nationwide coordinate and address-level GIS Dataset designed for precision in broadband planning, infrastructure deployment, and policy analysis. It includes over 115 million Broadband Serviceable Locations (BSLs), individual location structures where a broadband connection is or can be installed, including residential, business, multi-dwelling units, community anchor institutions (CAIs), and agricultural location types.
Each location is assigned a universal unique ID, ensuring seamless integration with additional Datasets. The schema aligns with the National Broadband Serviceable Location Fabric, supporting the FCC’s Broadband Data Collection (BDC), National Broadband Map, NTIA’s BEAD, and other federal broadband funding initiatives.
Verified coordinate-level Data intelligence
This multi-faceted Dataset is optimized for use in GIS platforms, network planning software, SQL databases, and other analytical and visualization tools, offering the foundational intelligence required to efficiently inform broadband infrastructure strategies and operations with confidence.

Verified Accuracy
GIS & SQL Ready
Trusted by Experts
Data included
Expand the box below to see the data fields included. Click on the data category to see its description.
How CostQuest Identifies Broadband Serviceable Locations
To get pinpoint accuracy for all locations, CostQuest categorizes as Broadband Serviceable Locations; the team aggregates hundreds of millions of data points, applies statistical scoring, and managed crowdsourcing to identify the precise locations of virtually every structure that is a candidate for broadband.
Step 1: Start with a Geographic Frame of Reference
When looking for Broadband Serviceable Locations (BSLs), CostQuest starts by obtaining rich geospatial information across all 50 states and territories to create a geographic frame of reference to start the analysis. CostQuest uses parcel information to create the geographic frame of reference, or the “sandbox” to work from, to provide boundaries of where to look for a structure/building within a piece of geography. CostQuest then ties in additional data sources to further the team’s understanding of the land and building use within each geographic frame.
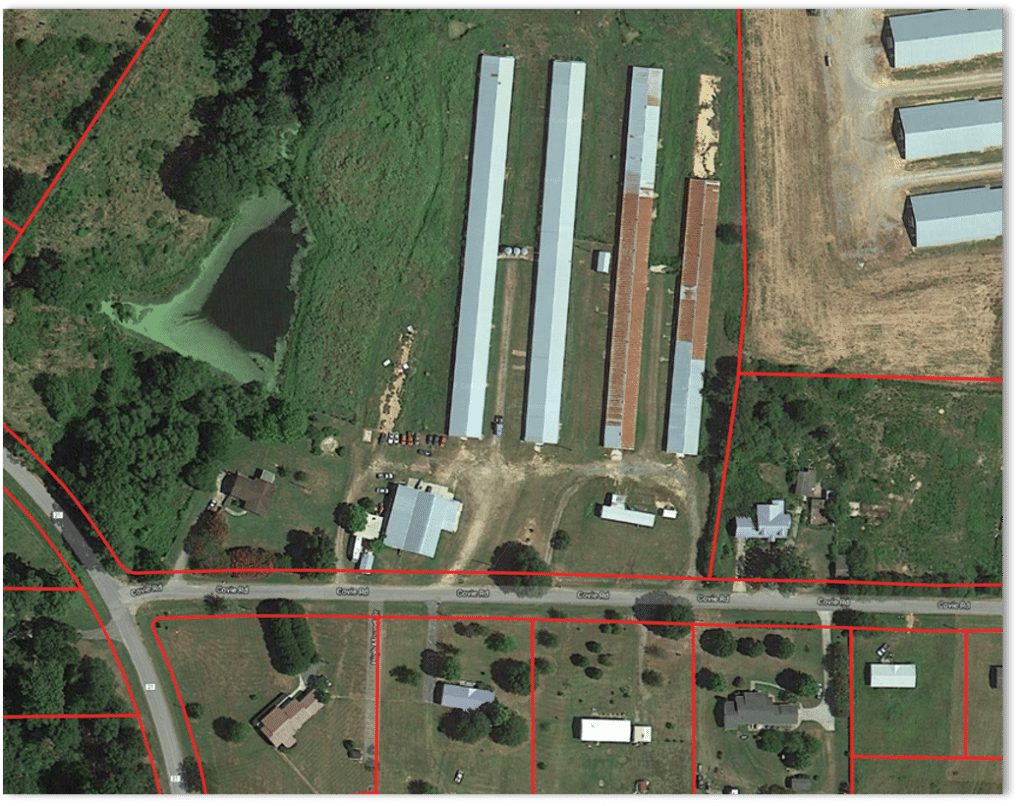
The red lines represent geographic frames of reference a.k.a. parcel boundaries.
Step 2: Link County Tax Assessor Information
County Tax Assessor attributes provide more details about a piece of geography – what it is used for, the address, the value of the property and any building on it, and more. By analyzing the tax attributes of each geographic frame of reference, CostQuest can isolate characteristics at a location level. Statistical scoring is used to systematically consider each attribute to answer a question: is this piece of geography likely to contain a structure that may require broadband service or a technical term CostQuest calls a Fabric Active structure?
Step 3: Connect Geographic Frames and Tax Assessor Information with Building Footprints
CostQuest then uses building footprints to look at all the possible buildings within each geographic frame of reference. These footprints give CostQuest the geospatial coordinates of each structure on that individual piece of property.
What CostQuest derives from the tax assessor attributes is then compared to what is seen in the building footprints. Rooftop detail, size, and building shape help us determine which building is the likely point where broadband service will be accessed. The structures are visually identified and assessed for confidence.
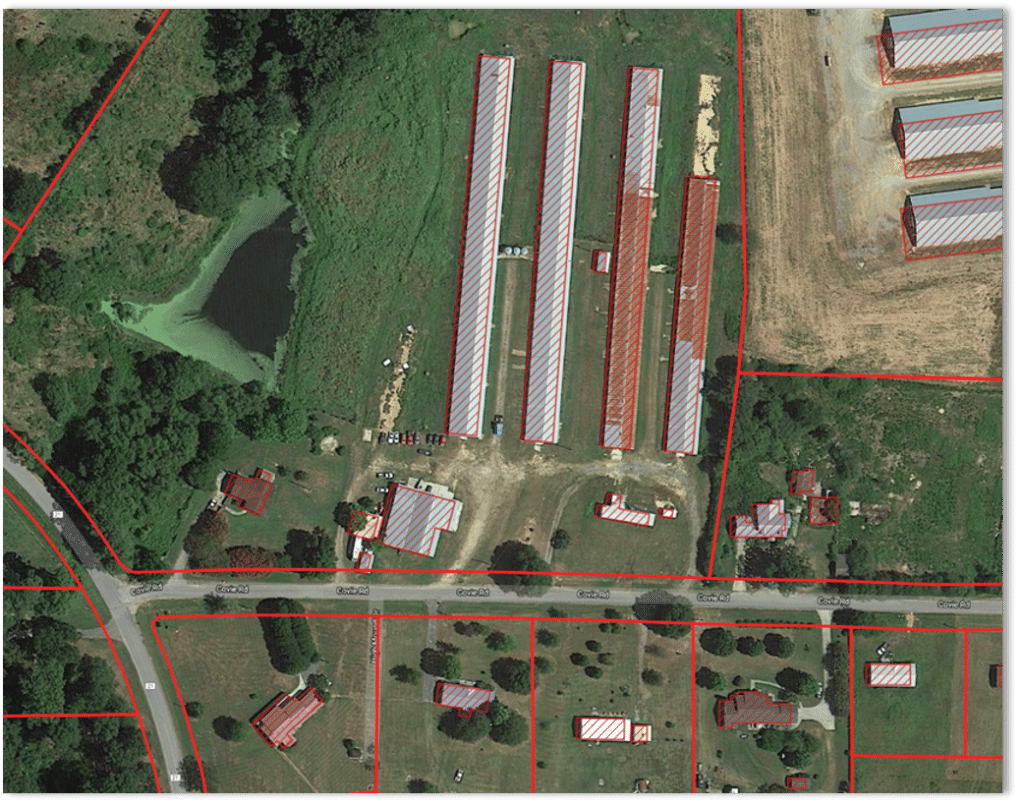
The red-shaded shapes above each location structure represent the building footprint.
Step 4: Connect other data sources
A. CostQuests connects additional data sources using a universal location identifier tied to each Broadband Serviceable Location to help inform the model as to which location structures are candidates for broadband. The data sources are updated semi-annually. The base data sources include:
Parcels
Satellite Imagery
Building footprints
Tax Attributes
Address datasets
Road Segments
US Census
B. More data can be linked to the locations to learn more about specific areas of interest. For example, broadband service availability, deployment cost information, federally funded locations, build complexity, demographics, and the competitive landscape.
Step 5: Identify Broadband Serviceable Locations
Final Result: Using conditional logic, CostQuest sets rules that connect building footprints from aerial imagery, tax attributes, road segments, U.S. Census, parcels, addresses, land cover data, and more to pinpoint and display the precise coordinates of each Broadband Serviceable Location (structure) that is the likely point where broadband service will be accessed.
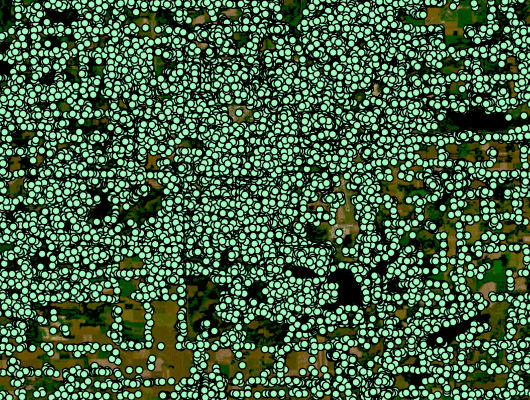
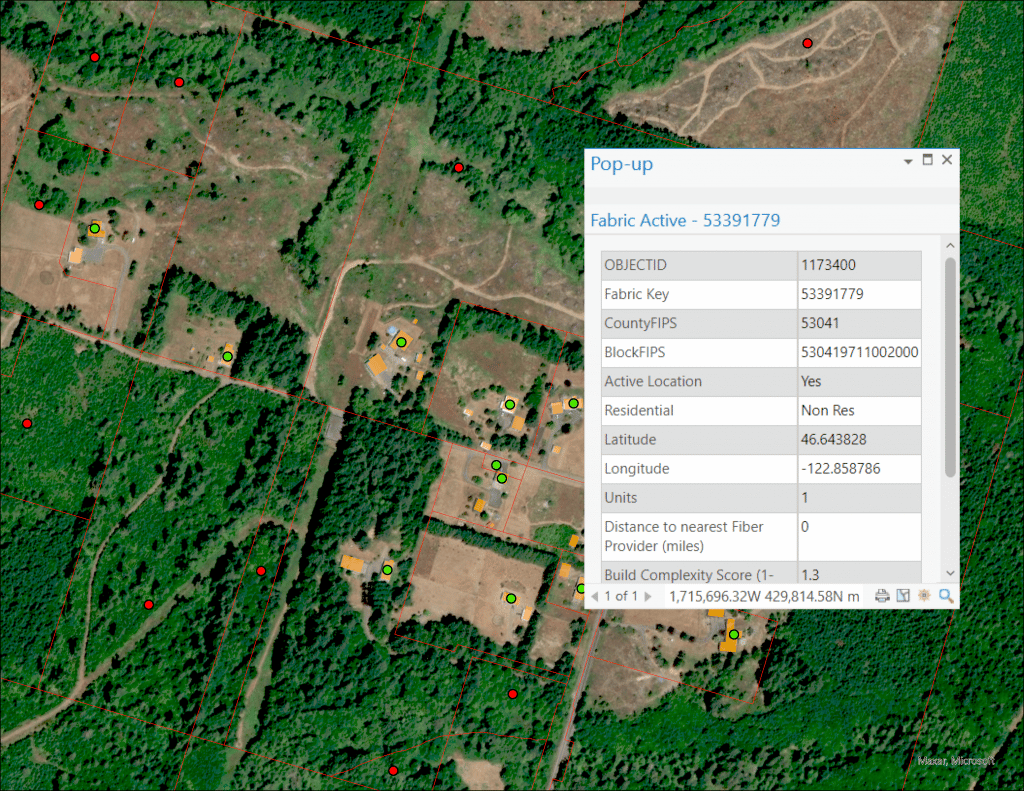
The circled locations with a green dot represent the identified Broadband Serviceable Location in each geographic frame of reference.
Step 6: Human Visual Verification
Visual verification is an internal process CostQuest uses to have human beings review locations that our models aren’t confident in. This step is critical in adding human oversight to improve machine learning in selecting the appropriate location structure within a geographic frame.
The circled locations with a green dot and check represent the identified and visually verified Broadband Serviceable Location in each geographic frame of reference.
Receive data in 3 easy steps
Step 1
Request sample data
Select “Get started today” located at the bottom of this page. Fill out the form and indicate you would like a sample in the comments field. Then, one of our sales representatives will reach out and set you up with a sample county.
Step 2
License the data you need
When you’re ready, license the data for your areas of interest and receive data via a secure portal. Choose a 1, 2 or 3 year license duration, with a minimum order size of a US County.
Step 3
Import-ready data files are delivered securely
We’ll deliver the BroadbandFabric data files via a secure portal, in .CSV file format for you to upload into any major GIS, SQL, or software of your choice. All orders come with access to our customer success team, to ensure you have what you need to be successful with the data.


