By: Zac Byrd, Marketing Associate & Hailey Farrow, Marketing Manager, on behalf of CostQuest Associates
What is the new Enhanced A-CAM program?
The Enhanced Alternative Connect America Model (Enhanced A-CAM) is a progressive iteration of its precursor, the A-CAM (Alternative Connect America Model), a funding program designed to address rural connectivity challenges within the broadband telecommunications sector. The new Enhanced A-CAM program sets forth a more ambitious and forward-looking framework for participating carriers to offer broadband and voice service at speeds of 100/20 Mbps (download/upload) or faster to all Enhanced A-CAM required locations within its study area (as determined by the National Broadband Map), compared to the previous A-CAM Program speed requirements of 25/3 Mbps, (FCC Report & Order).
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has delineated that the Enhanced A-CAM initiative allocates a substantively augmented financial pool for deployment endeavors and an extended timeframe for providers to execute broadband and voice service deployments.
Enhanced A-CAM support will be offered to all current A-CAM support recipients and prevailing rate-of-return carriers eligible to receive legacy support. The program entails a 15-year support tenure, starting on January 1st, 2024, and concluding on December 31st, 2038. In adherence to the prescribed timeline, carriers are obligated to formalize their participation choice no later than October 1st, 2023.
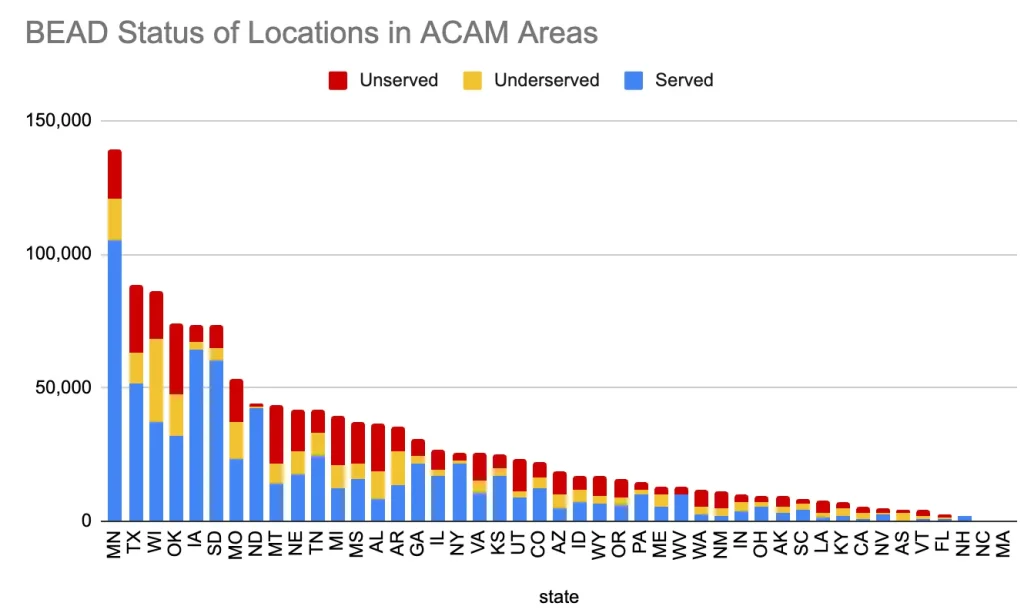
Enhanced A-CAM & BEAD Program Integration
The primary purpose of Enhanced A-CAM is to synchronize study areas with the Broadband, Equity, Access, and Deployment (BEAD) program funding initiatives. This alignment is aimed at preventing redundant funding efforts and potential strategic manipulation within the same geographical zones.
There are two ways Enhanced ACAM aligns with the NTIA BEAD funding program:
- The locations are based on Version 2 (V2) of the National Broadband Map to align with the locations under the BEAD program.
- The timeline is the same as outlined by the NTIA for BEAD locations – 4 years.
The eligible Enhanced ACAM areas will be excluded from BEAD eligibility due to their receipt of Enhanced A-CAM funding. This alteration is anticipated to enhance the efficacy of BEAD funds in expanding coverage. Telecom analyst Mike Conlow highlights, “If all ISPs accept the Enhanced A-CAM offer and build fiber, cable, or licensed fixed wireless, that takes 582,675 locations off the board for the BEAD program,” (Mike Conlow’s Newsletter).
Source: Mike Conlow’s Newsletter
Enhanced A-CAM Funding Structure
The Enhanced A-CAM program will offer no more than $1.27B annually, or 1.33B annually (if certain conditions are not met) over a 15-year term, beginning January 1st, 2024. The Wireline Competition Bureau (WCB) can increase the annual budget to deploy more services and provide support in the case of updates to the National Broadband Map.
On August 30th, 2023, the FCC announced the offers of model-baesd A-CAM support based on a revised version of the Alternative Connect America Cost Model (A-CAM). “Carriers have until Friday, September 29, 2023, to indicate, on a state-by-state basis, whether they elect to receive Enhanced A-CAM support,” (FCC’s Public Notice).
“The model results and offer amounts we release today are predicated upon carriers receiving support for Enhanced A-CAM required locations calculated using a monthly funding threshold of $63.69, a funding cap per location of $350, and an alternative funding percentage of 80%, except that required locations in Tribal lands are subject to a funding threshold of $47.76 and a funding cap of $365.93,”(FCC’s Public Notice).
Read the FCC’s Full Public Notice for more detailed information.
Enhanced A-CAM Program Eligibility & Requirements
Under the previous A-CAM program, eligibility was based on areas lacking services at speeds of 25/3 Mbps. Financial allotments were contingent on the beneficiary’s implementation of such service thresholds. Additionally, recipients were not required to extend coverage to every unserved location in their designated service area.
With the new Enhanced A-CAM, areas lacking a speed of 100/20 Mpbs will be eligible for funding, and recipients are required to deploy services to all eligible locations.
As a requirement of Enhanced A-CAM, carriers are required to make efforts to avoid duplicative broadband funding from federal programs.
- Recipients of the Enhanced A-CAM program must actively engage in BEAD program assessments and state-led challenge processes to determine support eligibility. They are also required to collaborate with States, Tribes, and other eligible entities to prevent redundant federal broadband funding efforts. Yearly certification of compliance is mandatory.
- Carriers must not use the BEAD program or future federal grant funds for the same area they are receiving Enhanced A-CAM support. This rule ensures proper use of support in line with the program goals. Enhanced A-CAM recipients can pursue BEAD funding for areas not covered by them due to competition and for other federal funding in non-eligible areas.
- When electing Enhanced A-CAM, carriers must specify the broadband technologies they plan to use for meeting their deployment obligations. This data allows states and Bead Program entities to identify, “which areas remain eligible for BEAD program funding,” (FCC Report & Order). This information is also pertinent to other federal broadband funding programs.
Affordability Requirement for Enhanced A-CAM Recipients
It’s important to note that Enhanced A-CAM recipients are obligated to participate in the Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP) as a requirement for obtaining support. The ACP serves as a crucial avenue for making affordable internet services available to low-income consumers.
As an integral part of the Enhanced A-CAM offer and a stipulation for receiving support, carriers must annually certify their participation in ACP or a comparable successor program. Failure to sustain ACP participation will be considered non-compliance with obligations.
Enhanced A-CAM Modeling
For Enhanced A-CAM offers, the FCC will use cost estimates from, “an updated version of A-CAM that incorporates the location data from the Broadband Serviceable Location Fabric Version 2 (the location data underlying the National Broadband Map) to calculate the average cost per location in each census block served by an A-CAM or CAF BLS recipient,” (FCC Report & Order). In accordance with the Broadband Data Act, following the establishment of the Broadband Serviceable Location Fabric and its accompanying maps, the FCC is mandated to incorporate these maps in the process of awarding funds for broadband internet access deployment.
The Broadband Data Act does not specify a cost estimate methodology, but the FCC notes that cost estimates derived from the existing A-CAM model would be exceptionally challenging to harmonize with the broadband coverage data originating from the Fabric and the National Broadband Map.
The previous version of A-CAM used census block boundaries from 2010, whereas the Fabric data employs 2020 census block boundaries. This leads to significant differences in the census block location counts, including blocks lacking model-estimated costs but having Fabric locations. The FCC suggests recalibrating the model with Fabric locations to enhance accuracy and reduce reconciliation for cost estimations for unserved/underserved locations.
Resources:
Disclaimer
This communication does not reflect the opinion or the policy of the Federal Communications Commission (FCC). The FCC is not responsible for the information or views in this communication and is not responsible for the accuracy, completeness, or timeliness of such information or views.